If you’re buying or selling a used car in the United Kingdom, learning how to check the VIN number is one of the first things you can do. With a VIN check, you can confirm the car’s identity and see the hidden risks and records before you pay a deposit.
If you want to find your VIN as well as the history of your car, Smart Car Check makes this quick and clear, with data pulled from trusted sources.
- A Vehicle Identification Number is a unique 17-character code that acts as a vehicle’s fingerprint. It shows details about the manufacturer, model, engine, year, and production plant.
- The VIN can be located in several places, including the dashboard near the windscreen, the driver’s door frame, the chassis/frame, or the paperwork.
- You can easily check the VIN by using the VIN Check tool and inputting the VIN on the form; you will see a comprehensive overview of the vehicle’s record history.
What is a VIN?
Think of a Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) as the vehicle fingerprint. It’s unique, permanent, and absolutely critical to its history. Before 1981, there wasn’t a standardized format for vehicle identification. Manufacturers used their own internal codes, and tracking a vehicle across countries was a logistical nightmare for DVLA and insurance companies.
This 17-character VIN number is required for all vehicles, and its presence is checked during MOT inspections for vehicles first used on or after 1 August 1980. This string of numbers and letters isn’t just random code generated by a computer. It contains specific, coded details about a vehicle’s manufacturer, model, and year of production, and helps authorities track vehicles for registration, taxation, and law enforcement purposes.
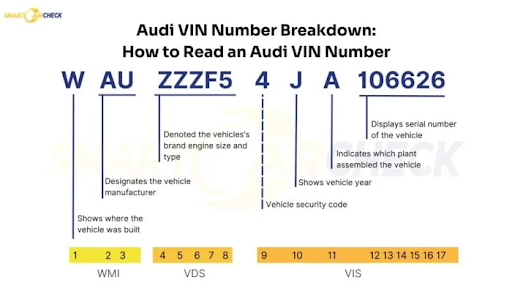
The VIN itself is split into three parts, which are:
WMI (World Manufacturer Identifier)
The first three characters of the VIN are known as the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI). This section tells you broadly where the vehicle was built and who built it. It’s a quick way to verify if a seller is being truthful about a car’s origins, especially with models that are manufactured in multiple countries.
VDS (Vehicle Descriptor Section)
Positions 4 through 8
The next five characters make up the Vehicle Descriptor Section. This is where things get specific about what vehicle you’re checking. This sequence describes the vehicle’s model, body style, engine type, and transmission. For mechanics and parts dealers, this section is gold. It confirms exactly what engine was installed at the factory.
Position 9
Position 9 is unique. It’s the “Check Digit.” It doesn’t tell you about the car’s features. Instead, it is used to verify the authenticity of the VIN itself. If someone tries to fake a VIN by changing a digit to hide a salvage history, the math won’t add up, and the check digit will appear invalid in a database. It’s a subtle but brilliant failsafe against fraud.
VIS (Vehicle Identifier Section)
The final section, positions 10 through 17, is the Vehicle Identifier Section. This is what makes your specific car unique from every other one of the same make and model.
Position 10 (Model Year)
The 10th position tells you about the vehicle model year. Manufacturers use a rotating set of letters and numbers to designate the year. For example, “L” was 1990, “Y” was 2000, and “A” was 2010. Note that letters I, O, and Q are never used to avoid confusion with numbers 1 and 0.
Position 11 (Plant Code)
Position 11 is a plant code; it tells you exactly which factory the vehicle was assembled in. Each automaker has its own unique set of codes for its assembly plants.
Positions 12-17 (Production Sequence)
These numbers make up the final portion of the VIN. It represents the sequential number or serial number of that specific vehicle as it came off the line. Every manufacturer uses its own system for this section, and it often resets annually at each manufacturing plant.
Before you ask, “How do I check a VIN number?” the first step is to locate the VIN to begin the VIN check. If you are looking at a used car, we recommend checking at least two of these locations to ensure they match. You can usually find the VIN in these common spots:
Dashboard
Look through the front windshield on the driver’s side. The VIN is typically visible through the lower corner of the glass, on the instrument panel.
Driver’s side door
Open the driver’s door and look for a sticker or plate on the door frame, door jamb, or where the door latches shut.
Vehicle chassis/frame
The VIN is often stamped directly into the vehicle’s chassis. This is usually in the engine bay or on the frame itself, near the front of the car.
Paperwork
Your VIN will be listed on your vehicle’s registration certificate (V5C logbook) and on your insurance documents.
Other locations
Depending on the vehicle, the VIN may also be found on the front of the engine block, under the spare tire, or in a rear wheel well.
Because number plates can change, the VIN is the best way to confirm the car’s real identity.
Verifying the Format
Once you have located the VIN, check its format. A valid VIN is always 17 characters long for vehicles manufactured after 1981. If the VIN is shorter or longer, and not a classic pre-1981 car, this may indicate potential tampering or that the vehicle is not compliant with federal standards
How Do I Check a VIN Number on an Imported or Exported Car?
For cars that have been imported or exported, a chassis- or VIN-based check is even more important because plates and paperwork might have changed along the journey. A VIN check shows you the import or export records and dates, so you can ask the seller about reasons and verify compliance before making a deal.
Also, checking the VIN number helps you decode where a vehicle was built and its model details, which is useful when specs differ by market.
How Do I Check a VIN Number?
To check a VIN number, all you need to do is follow these steps:
1. Locate the VIN
Check the windscreen corner (driver’s side), the driver’s door frame sticker, or your V5C logbook.
2. Go to the Smart Car Check VIN Check page
Go to the VIN Check page and use the form provided. The tool will verify data with official UK databases and other trusted sources.
3. Enter the VIN
Type it carefully. If a character doesn’t match, you won’t get the right car.
4. Open your report
You’ll see the preview report, which includes clear Vehicle Specifications and logbook details. Upgrade to the full paid report to see the vehicle history records.
5. Decide with Confidence
Use the report to ask better questions, negotiate, or walk away from risky cars. If something looks odd, compare the VIN on the car with the VIN on the V5C, and ask the seller for evidence (e.g., invoices, repair reports, finance clearance letters).
Why should you run the VIN check before you buy a used car?
You should run a VIN check before buying a used car to protect yourself. This essential step verifies the car’s identity, unearths its full operational history, and keeps you far away from fraudulent or inherently problematic vehicles.
The VIN report clearly reveals if a car has been flagged as stolen, if it carries a detrimental title (like salvaged or flood-damaged), if it has a history of major collision repairs, or if there are still finance payments owed on it.
This level of detail is crucial for avoiding costly mechanical surprises later on, and it ensures you have the factual data needed to argue for a fair price. Here are the details of what a VIN check can show you and why it’s important:
Outstanding Finance
If a lender still owns the car, it can be repossessed even after you buy it. If the car has outstanding finance & agreement, your report will show the finance company, agreement type/number, dates, and a contact number so you can confirm settlement before paying. Use Outstanding Finance Check to see if the car has it.
Insurance Write-offs & Salvage History
Through the car write-off check and salvage check, you can see whether the vehicle was damaged beyond economical repair or declared a total loss by insurers. The check reveals the write-off category (A, B, S, or N), type of damage, and loss date. This helps you avoid unsafe or hard-to-insure cars.
Stolen or High-risk Markers
No one wants a stolen car. A stolen car check instantly flags cars recorded as stolen in the national databases. If you don’t check the car and accidentally buy a stolen car, it can be seized by the police without compensation. The report provides you with the instant answer on theft records, including dates, police force, loss type, and more.
Mileage Fraud
Mileage fraud is a serious issue that makes worn-out cars look newer and more valuable. A full mileage check from Smart Car Check compares readings across MOT tests, services, and ownership changes to show any inconsistencies. This prevents you from overpaying for a car that’s been “clocked” or had its odometer tampered with.
Logbook (V5C) Issues
Since fake logbooks are used in vehicle cloning scams, verifying the V5C issuance date and certificate number ensures that you’re dealing with the rightful vehicle and not a stolen or forged one. Confirm the vehicle’s identity and history by checking the logbook (V5C vehicle registration certificate).
Keeper History
By checking the previous owner, you can see how many people have owned the vehicles and when the ownership changed. A car that has had too many owners in a short time may be showing repeated problems or dissatisfaction. Understanding the keeper’s history gives you insight into how well the vehicle has been maintained.
MOT History
Review past MOT test results with the MOT history check. See the report details about the failures and advisory notes. This shows how well the car was cared for and what repairs might be due soon. It also helps you predict running costs and avoid buying a vehicle with a history of repeated mechanical failures.
Road Tax (Ved) Status & Expiry
A quick tax Check tells you whether the car is currently taxed and how much you’ll pay for renewal. Driving an untaxed car can lead to fines or legal trouble. The tax status section also shows the expiry date and the vehicle’s emissions band, helping you plan your yearly expenses.
Scrapped / Certificate of Destruction
Don’t waste money by buying a scrapped car that cannot even be driven on the road. The scrapped vehicle check lets you confirm if a car has been issued a Certificate of Destruction. Scrapped cars are meant to be dismantled permanently and are illegal to drive on UK roads. Buying one can lead to legal issues and safety risks, so this check is essential for peace of mind.
Auction Records
Cars sold at auctions often have complicated histories. The auction check shows the previous sales, images, title type, and damage descriptions. Knowing this helps you understand the car’s journey and avoid models that were damaged or sold off cheaply abroad.
Vehicle Specs, MPG, and ULEZ Status
It’s important to know the car’s accurate specifications, such as fuel economy (MPG), performance (BHP), and ULEZ compliance. These details, available through the MPG Check, BHP Check, and ULEZ Checker, help you calculate long-term fuel costs and confirm if the car meets city clean-air standards.
Common Red Flags a VIN Check Shows To You
If any of these red flags appear in your report, pause the deal and ask for proof. These are the issues that often lead to regret.
Outstanding finance is attached to the vehicle.
In the UK, debt stays with the vehicle, not the person. If the previous owner stopped making payments on their PCP or HP agreement, that car is technically stolen property the moment they sell it to you.
If you ignore this flag, you will lose the car and the money. The law rarely sides with the “good faith” buyer here. So, if you see one, do not hand over a penny until the seller provides a clearance letter from the lender.
Written off
Being written off in a car means that the vehicle is less valuable. Even with repairable damage to the vehicle, whether structural (Category S) or non-structural (Category N), it can still affect safety/insurance.
Recorded as stolen or high-risk
Thieves steal a car, then find a legitimate car of the same make, model, and colour. They copy the legitimate car’s number plates and sometimes even forge a V5C logbook. If you see these records, walk away and contact the seller for proof.
Mileage rollback
If the vehicle has mileage rollback or inconsistent MOT mileages, it can lead to odometer fraud. Sellers often claim these issues as “the engine was replaced” or “the dashboard broke.” Don’t buy it without hard paperwork proof.
Scrapped status or V5C anomalies
Never buy a car that has a Certificate of Destruction. A scrapped car is not an asset but a liability. Don’t fall in love with the shiny paintwork until you’ve seen the car’s rap sheet. If you spot these red flags, walk away. There’s always another car.
Tips to Use Your VIN Check Report Like a Pro
To get the most value from your VIN check, apply these practical tips. They take only a few minutes and can save you from expensive surprises.
- Match everything: Make sure the VIN that you have in the car matches the paperwork.
- Call the finance company if there’s outstanding finance; get written confirmation of full settlement before purchase.
- Read MOT advisories to estimate near-term repair costs (tyres, brakes, suspension).
- Check plate and keeper changes together; many changes in a short period may suggest hidden problems.
- Keep screenshots/PDFs of the report when you negotiate the price.
Common Misconceptions and Challenges
When it comes to VIN checks, there are several myths that often confuse buyers. These misconceptions can create a false sense of security or cause people to skip important checks. Understanding the truth behind VIN inspections helps ensure you make better, safer decisions when evaluating a vehicle.
Misconceptions About VIN Checks
A lot of people assume VIN checks are only for second-hand cars, but even brand-new vehicles can have paperwork inconsistencies that need attention. Another misunderstanding is that VIN inspections are costly and unnecessary. In reality, running a car check at Smart Car Check is more affordable compared to the losses that can come from buying a car with hidden issues.
Many also think they can handle a VIN check on their own. While you can look at the VIN physically, a proper inspection requires access to professional databases and records. That’s why having an expert perform the check is essential if you want accurate results.
Challenges in Conducting VIN Checks
VIN checks rely heavily on real-time information sharing and consistent standards across different regions. This can be difficult without strong cooperation between police, manufacturers, and private partners. Smart Car Check helps bridge this gap by pulling data from trusted sources, making the process much simpler for buyers.
Advanced anti-theft tech, GPS systems, and database vulnerabilities also create challenges. Criminals often exploit these weak points, which is exactly why using a reliable history service like Smart Car Check gives buyers an added layer of protection.
Conclusion On How To Check VIN Numbers
In conclusion, knowing how to check the VIN is important when considering purchasing a used vehicle. It helps ensure that you have accurate information about the vehicle’s history, including the mileage history, theft reports, MOT history, auction records, and other crucial details.
Running a complete car check allows you to buy with confidence by understanding the vehicle’s true history and identity and protects you from potential problems, ensuring your car purchase goes smoothly from start to finish.
FAQ about How To Check VIN Number
Is a VIN 16 or 17 digits?
All vehicles manufactured after 1981 must have a 17-character VIN. If your VIN is shorter (and the car isn’t a pre-1981 classic), this may indicate tampering, errors, or identity fraud.
What if my VIN is less than 17 digits?
If your VIN is shorter than 17 characters on a modern vehicle is a red flag. It may signal tampering, cloning, plate-swapping, or that the vehicle is not compliant with UK standards. Smart Car Check can help verify discrepancies by comparing VIN records with official UK databases to confirm authenticity.
How do I check if a VIN is legit?
A legitimate VIN (isn’t a pre-1981 classic) should:
- Be exactly 17 characters
- Contain no I, O, or Q
- Match the VIN on the V5C
- Match vehicle spec revealed in a Smart Car Check VIN report
If the vehicle details in the report do not match the car you’re viewing, the VIN may be altered.
What do the first 3 digits of a VIN mean?
The first three characters are the WMI (World Manufacturer Identifier), and the first 3 digits of a VIN mean a vehicle type or manufacturing division, depending on the first and second digits of the WMI. (e.g., “WVW” for Volkswagen Germany).
What do digits 12–17 in a VIN indicate?
Digits 12–17 represent the Vehicle Identifier Section (VIS). They usually include the vehicle’s production sequence or serial number. Smart Car Check automatically decodes this section for you.
Which digit in the VIN is the engine?
Engine information typically appears within digits 4–8 of the VIN, depending on the manufacturer. Smart Car Check shows you the exact engine details in your VIN report in seconds by entering your VIN into our tools.
That’s a huge benefit; it gives you a buffer to handle any minor defects or advisories without having to drive illegally, and the new certificate still gives you a full 12 months of coverage.
Is it safe to share my VIN number?
Yes. A VIN is not secret information. Mechanics, insurers, dealers, and history-check services use it daily. However, never share personal documents, and only share the VIN itself.
Can two cars have the same VIN number?
No. A VIN must be unique for each vehicle. If two cars share the exact VIN number, one of them is likely a clone or a fraudulent vehicle.